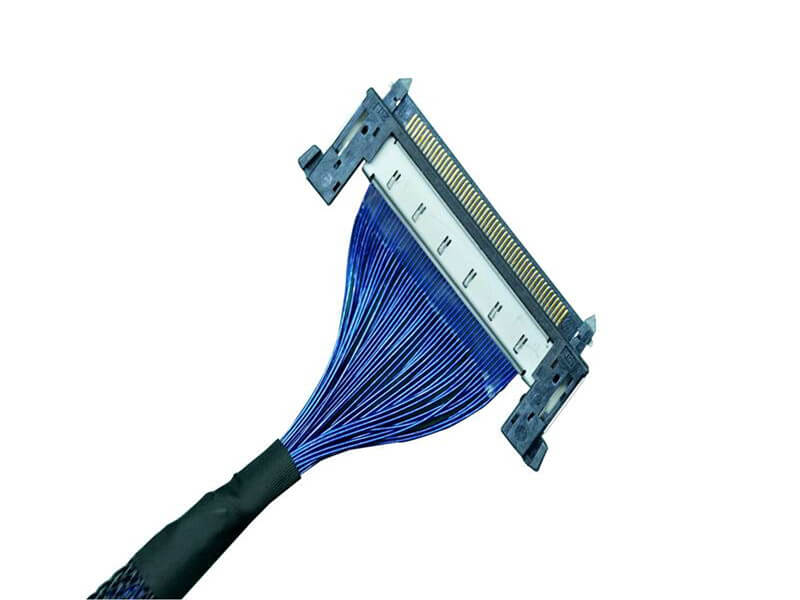
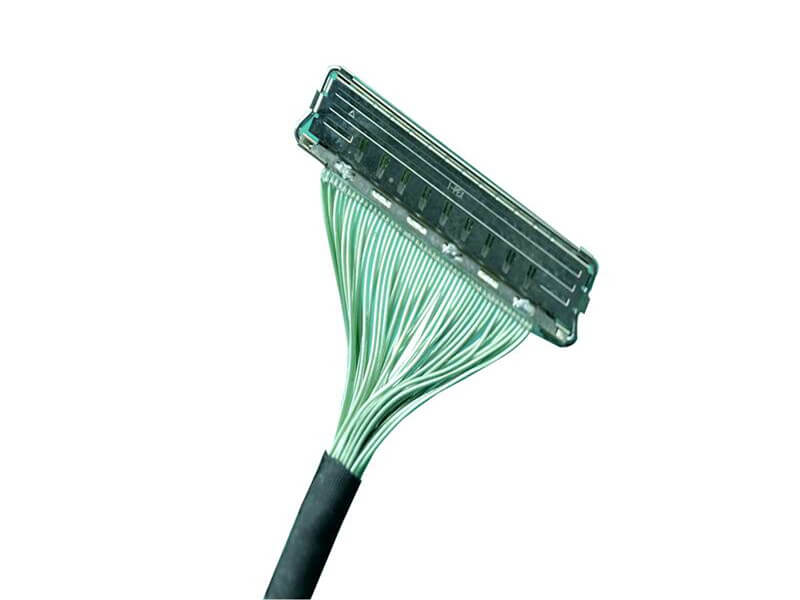
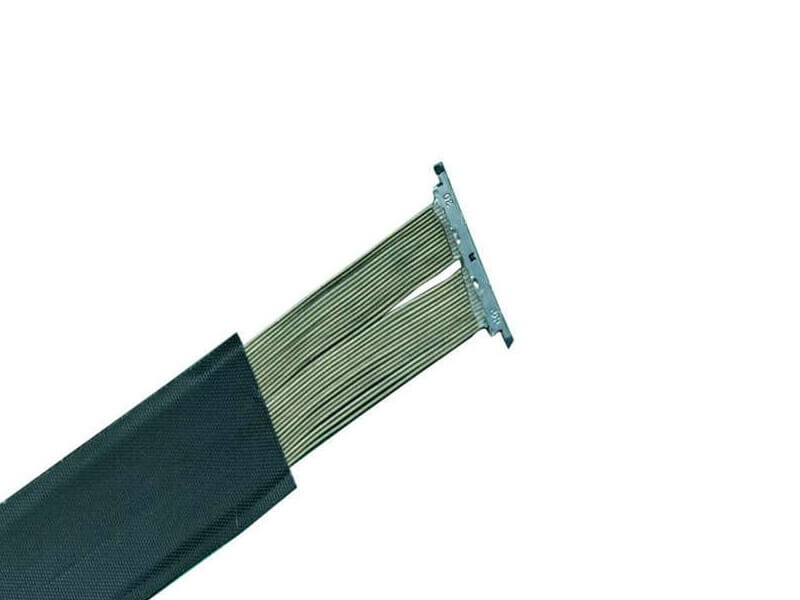
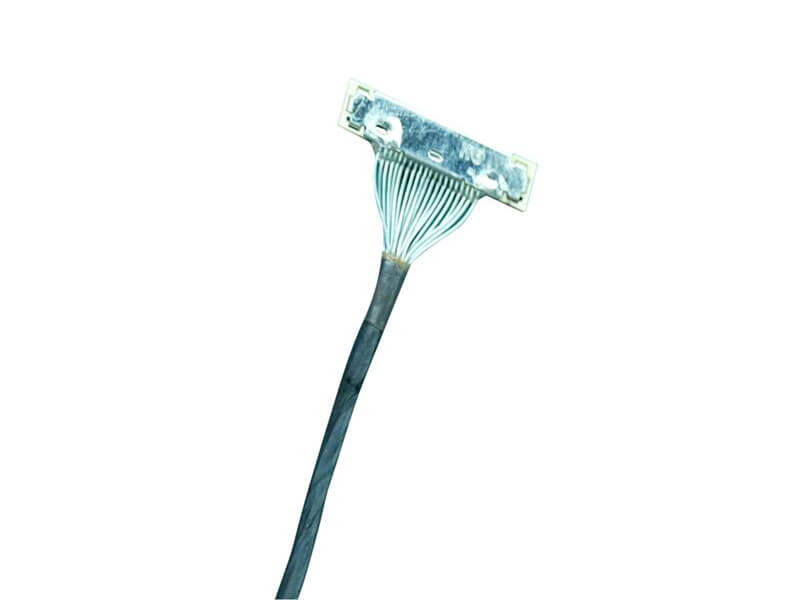
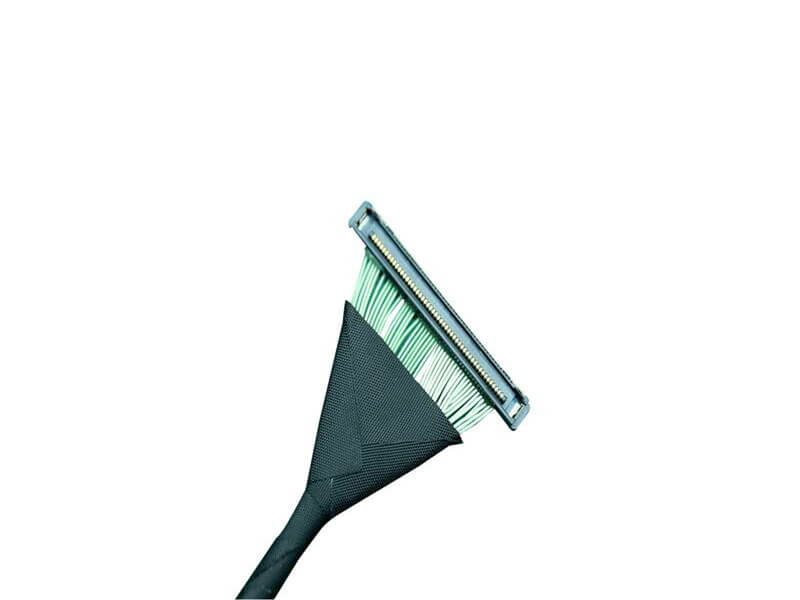
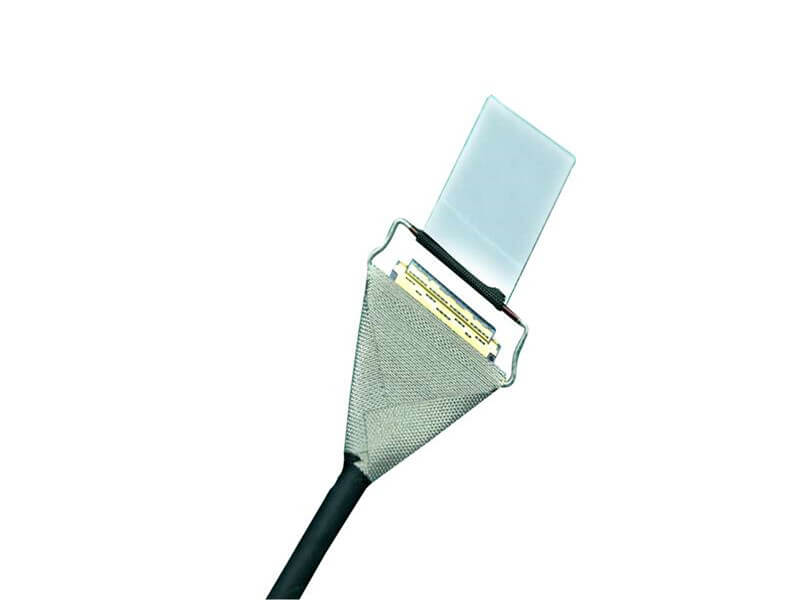
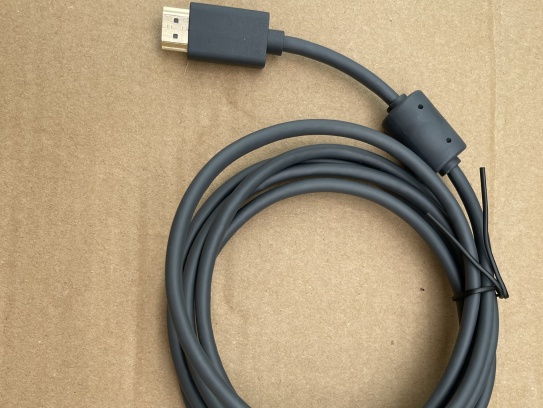
As 5G New Radio (NR) networks push into FR2 bands—spanning 24.25 GHz to 40 GHz and beyond—the performance of every interconnect in the RF front-end is under unprecedented scrutiny. Among these, the micro coaxial cable termination solutionis a critical yet often underestimated factor. In high-frequency systems, even minor impedance mismatches can lead to significant signal reflection, degrading modulation accuracy and overall link budget. This article introduces a new termination approach engineered to achieve ultra-low VSWRfor 5G mmWave modules, addressing the signal integrity, manufacturability, a.
Read more →Key Parameters Defining Transmission Performance1.1 Frequency Range and BandwidthMicro-coaxial cables are optimized for high-frequency signal transmission, typically supporting frequencies from DC to 40 GHz or higher. Their bandwidth depends on: Conductor Design: Solid or stranded copper cores (often silver-plated) reduce skin effect losses at high frequencies.Dielectric Material: Low-loss insulators like PTFE (εr ≈ 2.1) or foamed polyethylene minimize signal attenuation.For example, ultra-miniature cables (0.3 mm diameter) used in 5G mmWave applications maintain a bandwidth of 50 G.
Read more →Microwave links play a pivotal role in modern communication systems, enabling high-speed data transmission across long distances without the need for physical fiber-optic cables or terrestrial wiring. From telecommunications networks and satellite communications to radar systems and industrial automation, these links depend heavily on components that can maintain signal integrity, minimize loss, and withstand diverse environmental conditions. Among these critical components, micro-coaxial cables stand out as a cornerstone, offering unique advantages that make them indispensable for microwave link appl.
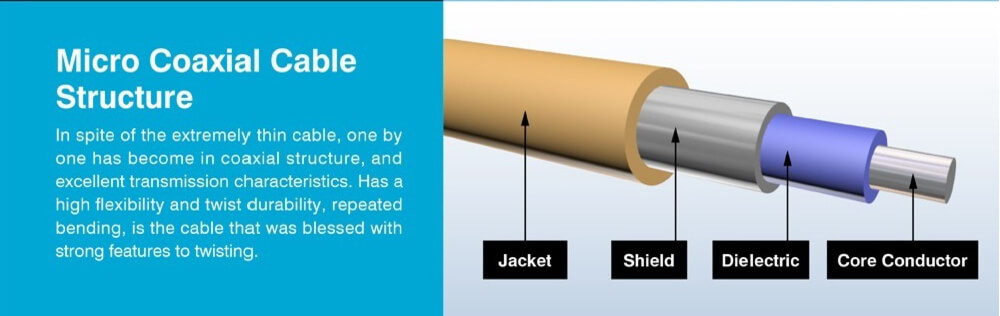
Read more →In the vast world of underwater connectivity, coaxial cables play a pivotal role in ensuring seamless submarine communications. This article will explore the importance, functionality, and considerations of coaxial cables in submarine communication systems. How Coaxial Cables Work Coaxial cables consist of a central conductor, surrounded by an insulating layer, a shielding layer, and an outer jacket. This design allows for efficient transmission of electrical signals with minimal interference. In submarine applications, the coaxial structure is especially crucial as it helps in maintaining signa.
Read more →Meta Description: Discover aviation-grade fire-resistant micro-coaxial cables engineered to exceed FAA & EASA flammability requirements. Ideal for aircraft wiring, UAVs, and mission-critical systems. Next-Gen Fire Safety in Aviation Wiring The aerospace industry faces relentless pressure to enhance safety while reducing weight and complexity. A breakthrough emerges with new fire-resistant micro-coaxial cables engineered specifically to comply with aviation standards like FAA FAR 25.853 and EASA CS 25.853. These cables represent a critical leap in safeguarding aircraft el.
Read more →A significant milestone has been reached in our factory’s history as we proudly announce the successful mass production of our high – performance coaxial cables. This achievement is not just a result of months of hard work but also a testament to our commitment to technological innovation, quality control, and meeting the ever – growing demands of the market. Technological Breakthroughs Paving the Way The journey to mass production was filled with challenges, and overcoming them required significant technological breakthroughs. One of the key areas we focused on was the materia.
Read more →Can't find what you're looking for?
Our customer support team is ready to assist you with any questions or concerns.
Search FAQs
Related Articles
Coaxial Cable Production Cost Reduced by Our Factory
In recent years, our factory has achieved a significant reduction in the production cost of coaxial cables through a series of targeted me.
Effective Solutions for Excessive Signal Attenuation in Micro Coaxial Cables
Micro coaxial cables are widely used in high-frequency signal transmission, such as in telecommunications, medical devices, and aerospace .
Noise-Canceling Headphones: How Micro-Coaxial Wiring Supercharges Audio Clarity
You’re investing in noise-canceling (ANC) headphones for one primary goal: pristine audio in a noisy world. While features like driv.
Understanding Bend Radius Limitations for Micro Coaxial Cables
Micro coaxial cables are essential components in modern electronics, enabling high-speed signal transmission in compact devices like smart.
Quantum Computing Breakthroughs Enabled by Cryogenic Micro-Coaxial Cables
The race towards practical quantum computing hinges on overcoming immense technical hurdles. Among the most critical is the challenge of r.
Customizable Coaxial Cable Lengths for Specific Installations
Coaxial cables are indispensable in a wide range of installations, including telecommunications, security systems, broadcasting, and home .